Microsoft Internet Security and Acceleration (ISA) Server 2000 is Microsoft’s firewall and proxy server product, replacing Microsoft Proxy Server.
ISA Server 2000 operates in one of three modes:
- Firewall – security server.
- Caching (i.e. proxy) – acceleration server.
- Integrated – firewall and caching.
As a firewall, ISA Server’s filtering capabilities include:
- Packet filtering (layer 3) capabilities – filtering based on the source and destination IP addresses along with their respective port numbers.
- Circuit (TCP) and stateful inspection (UDP) filtering – filtering bases on a sequence of packets (e.g. to guard against denial of service attacks).
- Application filtering (layer 7) – actually inspecting the data segment of the packet.
(layer numbers refer to the open system interconnection 7 layer network model).
The product can be used as an internal or external firewall and ISA Server 2000 achieved certification for Common Criteria Evaluation Assurance Level 2 (EAL 2) in September 2003.
ISA Server’s basic caching (proxy) process is as follows:

- Client requests access to an external website. Because the DNS suffix address is not local, it knows to contact the proxy server.
- ISA Server receives the request and checks its cache, which by default is split between 50% of the ISA server’s available memory (fast) and disk (slower).
- If there is no match in the cache, then space is reserved in cache and the request is forwarded to the Internet, using network address translation (NAT).
- The external web server replies with the requested page.
- The reply is cached with a time to live (TTL) (default 24 hours) and is forwarded to the requesting client.
Other caching features include:
- Active caching – as the TTL for a cached resource expires, ISA server proactively fetches the latest copy of the resource from the Internet, storing it in the cache and accelerating future requests by keeping the latest versions of the most popular sites in the cache.
- Scheduled download – caching defined URLs on a schedule, e.g. caching a partner’s website each day for local access. This is most useful in a business to business (B2B) extranet scenario, where the content expiry can be predicted.
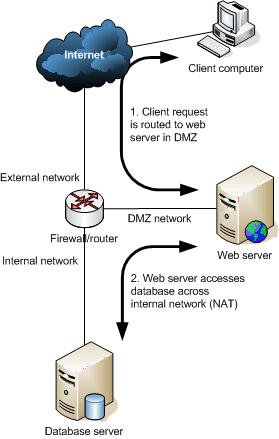
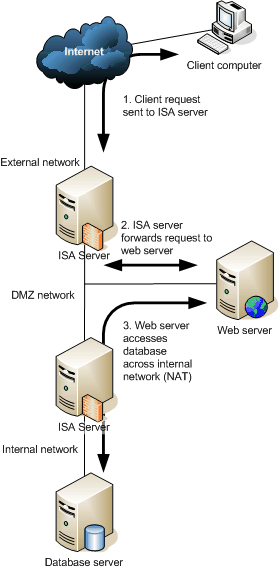
ISA server also supports VPN access (available in Windows 2000, XP and Windows Server 2003, but enhanced with ISA Server) and reverse publishing (allowing access to internal resources from the Internet). Reverse publishing using ISA Server is more secure than simply hosting a web server in a demilitarised zone (DMZ) as there is a firewall with NAT between the Internet and the DMZ, as well as between the DMZ and any internal resources.
Standard 3-pronged firewall with web server in DMZ:
Reverse publishing using ISA Server:
The configuration of ISA Server 2000 is controlled using policy elements, which are bundled together to create rules.
ISA Server 2000 Enterprise Edition allows the formulation of arrays of ISA servers, providing greater scalability.
Links
Microsoft ISA Server
Microsoft ISA Server firewall and cache resource site
One thought on “10,000 feet view of Microsoft ISA Server 2000”